Polyethylene has various product types based on polymerization methods, molecular weight levels, and degree of branching. Common types include high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE).
Polyethylene is odorless, non-toxic, feels like wax, has excellent low temperature resistance, good chemical stability, and can withstand the erosion of most acids and alkalis. Polyethylene can be processed using injection molding, extrusion molding, blow molding, and other methods to produce products such as films, pipes, wires and cables, hollow containers, packaging tapes and ties, ropes, fish nets, and woven fibers.
The global economy is expected to decline. Against the background of high inflation, consumption is weak and demand is reduced. In addition, the Federal Reserve continues to raise interest rates, monetary policy is tightened, and commodity prices are under pressure. In addition, the Russia-Ukraine conflict continues and the prospect is still unclear. The price of crude oil is strong, and the cost of PE products is still high. In recent years, PE products have been in a period of continuous and rapid expansion of production capacity, and downstream end product enterprises have been slow to follow up on orders. The supply-demand contradiction has become one of the main problems in the development of the PE industry at this stage.
Analysis and Prediction of World Polyethylene Supply and Demand
The world’s polyethylene production capacity continues to grow. In 2022, the world’s polyethylene production capacity exceeded 140 million tons per year, a year-on-year increase of 6.1%, with a year-on-year increase of 2.1% in production. The average operating rate of the unit was 83.1%, a decrease of 3.6 percentage points compared to the previous year.
Northeast Asia accounts for the largest proportion of world polyethylene production capacity, accounting for 30.6% of the total polyethylene production capacity in 2022, followed by North America and the Middle East, accounting for 22.2% and 16.4% respectively.
About 47% of the world’s polyethylene production capacity is concentrated in the top ten production enterprises with production capacity. In 2022, there were nearly 200 major polyethylene production enterprises in the world. ExxonMobil is the world’s largest polyethylene production enterprise, accounting for approximately 8.0% of the world’s total production capacity. Dow and Sinopec are ranked second and third respectively.
In 2021, the total international trade volume of polyethylene was 85.75 billion US dollars, a year-on-year increase of 40.8%, and the total trade volume was 57.77 million tons, a year-on-year decrease of 7.3%. From a price perspective, the average export price of polyethylene in the world is 1484.4 US dollars per ton, a year-on-year increase of 51.9%.
China, the United States, and Belgium are the world’s major importers of polyethylene, accounting for 34.6% of the world’s total imports; The United States, Saudi Arabia, and Belgium are the main exporting countries of polyethylene in the world, accounting for 32.7% of the total world exports.
The world’s polyethylene production capacity will maintain rapid growth. In the next two years, the world will add more than 12 million tons of polyethylene production capacity per year, and these projects are mostly integrated projects that are produced in conjunction with upstream ethylene plants. It is expected that from 2020 to 2024, the average annual growth rate of polyethylene will be 5.2%.
Current Situation and Forecast of Polyethylene Supply and Demand in China
China’s polyethylene production capacity and output have increased simultaneously. In 2022, China’s polyethylene production capacity increased by 11.2% year-on-year and production increased by 6.0% year-on-year. As of the end of 2022, there are nearly 50 polyethylene production enterprises in China, and the new production capacity in 2022 mainly includes units such as Sinopec Zhenhai Refinery, Lianyungang Petrochemical, and Zhejiang Petrochemical.
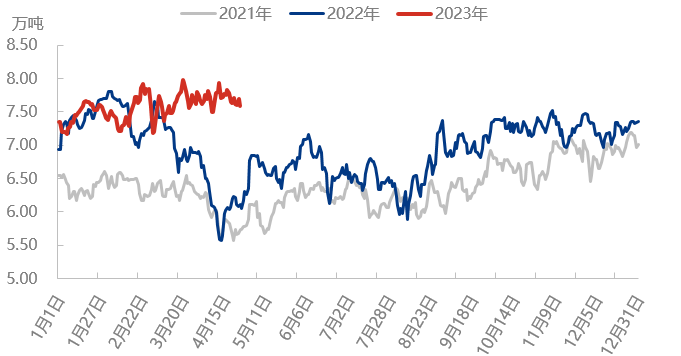
Comparison Chart of Polyethylene Production in China from 2021 to 2023
The increase in apparent consumption of polyethylene is limited, and the self-sufficiency rate maintains growth. In 2022, the apparent consumption of polyethylene in China increased by 0.1% year-on-year, and the self-sufficiency rate increased by 3.7 percentage points compared to the previous year.
The import volume of polyethylene in China decreased year-on-year, while the export volume increased year-on-year. In 2022, China’s polyethylene import volume decreased by 7.7% year-on-year; The export volume increased by 41.5%. China remains a net importer of polyethylene. China’s polyethylene import trade mainly relies on general trade, accounting for 82.2% of the total import volume; Next is import processing trade, accounting for 9.3%. Imports mainly come from countries or regions such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates, accounting for approximately 49.9% of the total imports.
Polyethylene is widely used in China, with film accounting for over half of the total. In 2022, thin film remains the largest downstream application field of polyethylene in China, followed by injection molding, pipe profiles, hollow and other fields.
China’s polyethylene is still in a stage of rapid growth. According to incomplete statistics, China plans to add 15 sets of polyethylene plants before 2024, with an additional production capacity of over 8 million tons per year.
2023 PE Domestic New Device Production Schedule
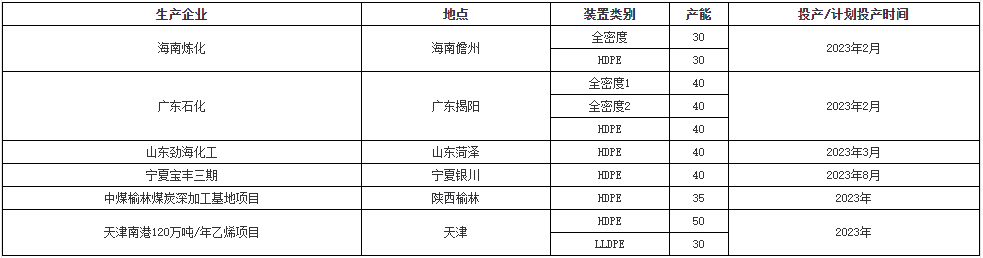
As of May 2023, the total production capacity of domestic PE plants has reached 30.61 million tons. In terms of PE expansion in 2023, it is expected that the production capacity will be 3.75 million tons per year. Currently, Guangdong Petrochemical, Hainan Refining and Chemical, and Shandong Jinhai Chemical have put into operation, with a total production capacity of 2.2 million tons. It involves a full density device of 1.1 million tons and a HDPE device of 1.1 million tons, while the LDPE device has not yet been put into operation during the year. In the second half of the following year, there are still 1.55 million tons/year of new equipment production plans, involving 1.25 million tons of HDPE equipment and 300000 tons of LLDPE equipment. It is expected that China’s total production capacity will reach 32.16 million tons by 2023.
At present, there is a serious contradiction between supply and demand of PE in China, with concentrated production capacity of new production units in the later stage. However, the downstream product industry is facing a stalemate in raw material prices, low product orders, and difficulty in increasing prices at the retail end; The decrease in operating income and high operating costs have led to tight cash flow for enterprises, and in recent years, under the background of high inflation, foreign monetary tightening policies have increased the risk of economic recession, and weak demand has led to a reduction in foreign trade orders for products. Downstream product enterprises, like PE products, are in a period of industrial pain due to supply and demand imbalance. On the one hand, they need to pay attention to traditional demand, while developing new demand and finding export directions have become
From the distribution proportion of downstream PE consumption in China, the largest proportion of consumption is film, followed by major product categories such as injection molding, pipe, hollow, wire drawing, cable, metallocene, coating, etc. For the film product industry, the mainstream is agricultural film, industrial film, and product packaging film. However, in recent years, the demand for traditional disposable plastic film products has been gradually replaced by the popularity of degradable plastics due to limited plastic regulations. In addition, the packaging film industry is also in a period of structural adjustment, and the problem of overcapacity in low-end products is still serious.
The injection molding, pipe, hollow and other industries are closely linked to the needs of infrastructure and daily civilian life. In recent years, due to factors such as negative consumer sentiment feedback from residents, the development of the product industry has faced certain growth obstacles, and recent limited follow-up on export orders has also led to the possibility of a slowdown in growth in the short term.
What are the growth points of domestic PE demand in the future
In fact, at the 20th National Congress at the end of 2022, various measures have been proposed to stimulate domestic demand, with the goal of opening up internal circulation in China. In addition, it has been mentioned that increasing urbanization rate and manufacturing scale will bring demand stimulation to PE products from the perspective of internal circulation promotion. In addition, the comprehensive relaxation of control, economic recovery, and expected increase in demand for internal circulation also provide policy guarantees for the future recovery of domestic demand.
Consumer upgrading has given rise to emerging demand, with higher requirements for plastics in fields such as automobiles, smart homes, electronics, and rail transit. High quality, high-performance, and environmentally friendly materials have become the preferred choice. The potential growth points for future demand are mainly in four areas, including packaging growth in the express delivery industry, packaging films driven by e-commerce, and potential growth in new energy vehicles, components, and medical demand. There are still potential growth points for PE demand.
In terms of external demand, there are many uncertain factors, such as China US relations, Federal Reserve policy, Russia Ukraine war, geopolitical policy factors, etc. Currently, China’s foreign trade demand for plastic products is still in the output of low-end products. In the field of high-end products, many expertise and technology are still firmly held in the hands of foreign enterprises, and the technology blockade of high-end products is relatively severe, Therefore, it is also a potential breakthrough point for China’s future product exports, where opportunities and challenges coexist. Domestic enterprises still face technological innovation and development.
Post time: May-11-2023